CFD Analysis of Hybrid Photovoltaic Thermal (PV/Th) Solar Collector Efficiency Incorporating Ag-AL2O3/water Hybrid Nanofluids
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69717/jaest.v5.i1.110Keywords:
Renewable energy, Solar energy, Hybrid Photovoltaic-Thermal solar collectors, PV panel, Hybrid nanofluid, CFD simulation, Heat and mass transferAbstract
The optimization of energy consumption is closely tied to enhancing the power output of photovoltaic panels. This study offers a numerical investigation of the utilization of hybrid nanofluids (Ag-Al2O3-water) as a cooling fluid in a hybrid photovoltaic thermal (PV/Th) collector, aiming to improve electrical performance by lowering the PV cells operating temperature. The hybrid PV/Th collector comprises a photovoltaic panel (PV) coupled with a thermal collector, including a heat sink equipped with rectangular ribs positioned at the bottom of the PV module. This research explores the impact of critical configuration parameters, such as inlet velocities of working fluid and nanoparticle volume fractions, on the Nu number, PV cell temperature, and both thermal and electrical efficiencies within steady-state operating conditions. The 3D numerical simulation to analyze the overall performance of a hybrid PV/Th collector was conducted using ANSYS Fluent software version 17.1. The numerical findings demonstrate that increasing the nanoparticle volume fraction elevates the cooling fluid's thermal conductivity, consequently enhancing the heat transfer by conduction. Furthermore, higher coolant velocities enhance heat transfer by convection, resulting in a more effective heat transfer rate within the PV/Th system. This, in turn, reduces the operating temperature and significantly enhances the hybrid PV/Th system's overall performance.
Highlights
- Hybrid nanofluid cooling reduces PV cell temp and boosts overall system efficiency.
- Higher Re numbers and nanoparticle loads enhance thermal and electrical performance.
- ANSYS CFD showed max total efficiency of 44.7% at Re = 800, Φ = 0.06.
- Ag-Al2O3 nanofluid outperformed water alone in PV/Th heat transfer.
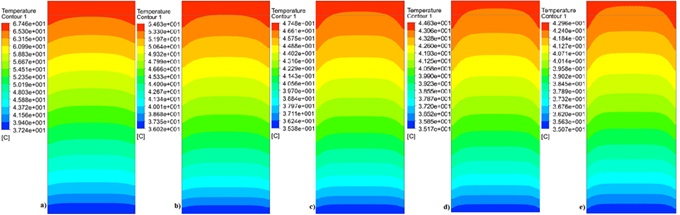
- PV cell temp dropped from 60.1°C to 40.6°C using nanofluid at high flow rate.
Downloads
References
M. Alktranee and P. Bencs, “Applications of nanotechnology with hybrid photovoltaic/thermal systems: A review,” J. Appl. Eng. Sci., vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 292–306, 2021. https://doi.org/10.5937/jaes0-28760.
L. Alboteanu, “Increase efficiency of stand-alone photovoltaic systems by reducing temperature of cells,” Ann. “ConstantinBrancusi” Univ. TarguJiu, vol. 3, pp. 195–204, 2011.
A. S. Abdelrazik, F. A. Al-Sulaiman, R. Saidur, and R. Ben-Mansour, “A review on recent development for the design and packaging of hybrid photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) solar systems,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 95, no. December 2017, pp. 110–129, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.07.013.
V. V. Tyagi, S. C. Kaushik, and S. K. Tyagi, “Advancement in solar photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) hybrid collector technology,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 1383–1398, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.12.013.
A. Tiwari, M. S. Sodha, A. Chandra, and J. C. Joshi, “Performance evaluation of photovoltaic thermal solar air collector for composite climate of India,” Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, vol. 90, no. 2, pp. 175–189, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2005.03.002.
C. Beldjani, N. Belghar, and K. Aoues, “Efficiency improvement of air-cooled photovoltaic modules utilizing copper heat dissipators,” Desalin. Water Treat., vol. 279, no. May, pp. 140–146, 2022. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2022.29099.
A. S. Joshi, A. Tiwari, G. N. Tiwari, I. Dincer, and B. V. Reddy, “Performance evaluation of a hybrid photovoltaic thermal (PV/T) (glass-to-glass) system,” Int. J. Therm. Sci., vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 154–164, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2008.05.001.
F. Sarhaddi, S. Farahat, H. Ajam, A. Behzadmehr, and M. Mahdavi Adeli, “An improved thermal and electrical model for a solar photovoltaic thermal (PV/T) air collector,” Appl. Energy, vol. 87, no. 7, pp. 2328–2339, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.01.001.
Z. Said, S. Arora, and E. Bellos, “A review on performance and environmental e ff ects of conventional and nano fl uid-based thermal photovoltaics,” vol. 94, no. October 2017, pp. 302–316, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.06.010.
E. Ebrahimnia-bajestan, M. Charjouei, and H. Niazmand, “International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer Experimental and numerical investigation of nanofluids heat transfer characteristics for application in solar heat exchangers,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., vol. 92, pp. 1041–1052, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2015.08.107.
T. Sokhansefat, A. B. Kasaeian, F. Kowsary, and M. Carlo, “Heat transfer enhancement in parabolic trough collector tube using Al 2 O 3 / synthetic oil nano fl uid,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 33, pp. 636–644, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.02.028.
K. Chadi, A. M. Kethiri, N. Belghar, B. Guerira, and Z. Driss, “CFD Simulation of the Heat Transfer using a Cuo-water Nano-fluid in Different Cross-sections of Mini-channels,” Mech. Eng. Technol. Appl., vol. 1, pp. 22–34, 2021. https://doi.org/10.2174/9789814998185121010004.
F. A. Sachit, M. Afzanizam, M. Rosli, N. Tamaldin, and S. Misha, “Nanofluids Used in Photovoltaic Thermal (PV/T) Systems : a Review“ vol. 7, no.3(20), pp. 599-611, 2018. https://doi.org/10.14419/ijet.v7i3.20.22950.
K. Chadi, N. Boultif, N. Belghar, A. Mohamed, Z. D. Kethiri, and B. Guerira, “Numerical Study of the Influence of Nano-fluid Type on Thermal Improvement in a Three Dimensional Mini Channel,” Mech. Eng. Technol. Appl., vol. 1, pp. 87–100, 2021. https://doi.org/10.2174/97898149981851210101.
M. Sardarabadi, M. Passandideh-fard, and S. Zeinali, “Experimental investigation of the effects of silica/water nano fl uid on PV/T (photovoltaic thermal units)” vol. 66, pp. 264–272, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.01.102.
H. A. Hussien, A. H. Noman, and A. Raad Abdulmunem, “Indoor Investigation for Improving the Hybrid Photovoltaic /Thermal System Performance Using Nanofluid (AL2O3-Water),” Eng. Technol. J., vol. 33, no. 4, pp. 889–901, 2015. https://doi.org/10.30684/etj.33.4a.12.
H. Fayaz, R. Nasrin, N. A. Rahim, and M. Hasanuzzaman, “Energy and exergy analysis of the PVT system : E ff ect of nano fl uid fl ow rate,” vol. 169, no. May, pp. 217–230, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.05.004.
M. S. Y. Ebaid, A. M. Ghrair, and M. Al-busoul, “Experimental investigation of cooling photovoltaic ( PV ) panels using ( TiO 2 ) nano fl uid in water -polyethylene glycol mixture and ( Al 2 O 3 ) nano fl uid in water- cetyltrimethylammonium bromide mixture,” Energy Convers. Manag., vol. 155, no. October 2017, pp. 324–343, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.10.074.
O. Rejeb, M. Sardarabadi, C. Ménézo, and M. Passandideh-fard, “Numerical and model validation of uncovered nanofluid sheet and tube type photovoltaic thermal solar system,” Energy Convers. Manag., vol. 110, pp. 367–377, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2015.11.063.
A. H. A. Al-waeli, K. Sopian, H. A. Kazem, and M. T. Chaichan, “Nano fl uid based grid connected PV / T systems in Malaysia : A techno- economical assessment,” vol. 28, no. January 2017, pp. 81–95, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2018.06.017.
Y. Khanjari, F. Pourfayaz, and A. B. Kasaeian, “Numerical investigation on using of nanofluid in a water-cooled photovoltaic thermal system,” Energy Convers. Manag., vol. 122, pp. 263–278, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.05.083.
S. Parvin, R. Nasrin, and M. A. Alim, “International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer Heat transfer and entropy generation through nanofluid filled direct absorption solar collector,” Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., vol. 71, pp. 386–395, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.12.043.
Ansys Fluent, “Ansys Workbench User’s Guide,” no. ANSYS, Inc, 2021, [Online]. Available: www.ansys.com.
G. Popovici, S. Valeriu, T. Dorin, and N.-C. Chereche, “Efficiency improvement of photovoltaic panels by using air cooled heat sinks,” vol. 85, no. November, pp. 425–432, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2015.12.223.
L. Boutina, K. Touafek, A. Khelifa, M. Lebbi, and M. T. Baissi, “Etude numérique sur l’amélioration du refroidissement d’un module photovoltaïque par l ’ utilisation des nanofluides,” Conference: SIENR 2018, At: Ghardaia, Algeria, pp. 1–6, 2018.
N. K. Baranwal and M. K. Singhal, “Modeling and simulation of a spiral type hybrid photovoltaic thermal (PV/T) water collector using ANSYS,” in Advances in Clean Energy Technologies: Select Proceedings of ICET 2020, Springer, pp. 127–139, 2021.
L. T. Wei, “A Simulation Study on Performance of Photovoltaic Thermal Water (PVTW) Collector Under Different Loading of Mass Flow Rate Using ANSYS Fluent,” Int. J. Nanoelectrics Mater., vol. 14, pp. 467–478, 2021.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Applied Engineering Science & Technology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.